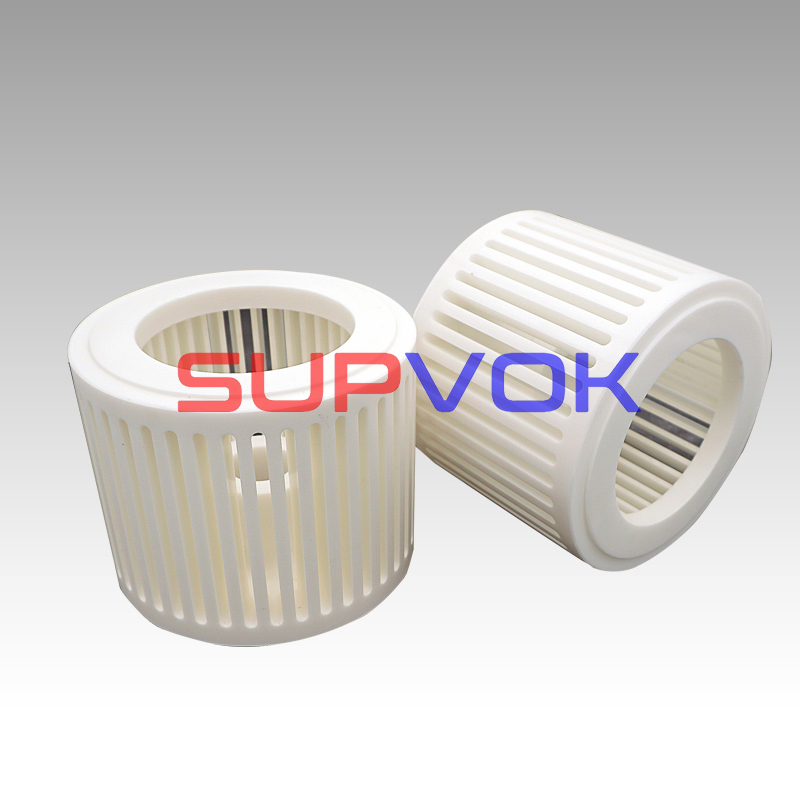
Customized Zirconia ceramic products
Application
In the aspect of functional ceramics, its excellent high temperature resistance is used as induction heating tubes, refractories and heating elements. Zirconia ceramics have sensitive electrical performance parameters and are mainly used in oxygen sensors, solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), high-temperature heaters and other fields. ZrO2 has a high refractive index (N-21 ^ 22). By adding certain coloring elements (V2O5, MoO3, Fe2O3, etc.) to the ultrafine zirconia powder, it can be made into colorful translucent polycrystalline ZrO2 materials, which can flash colorful light like natural gems, and can be made into various decorations. In addition, zirconia is widely used in thermal barrier coatings, catalyst carriers, medical, health care, refractories, textiles and other fields.
Zirconia is a special material, and the method of toughening is mainly achieved by the phase transformation of zirconia!
Pure zirconia is a white solid, which will appear gray or light yellow when containing impurities. Adding color developing agent can also display various other colors. The molecular weight of pure zirconia is 123.22, the theoretical density is 5.89g/cm3, and the melting point is 2715 ℃. It usually contains a small amount of hafnium oxide, which is difficult to separate, but has no obvious effect on the performance of zirconia. Zirconia has three crystal forms: monoclinic, tetragonal and cubic crystal phases. Zirconia only appears as monoclinic phase at room temperature, and will be transformed into tetragonal phase when heated to about 1100 ℃, and will be transformed into cubic phase when heated to higher temperature. Due to the large volume change during the transformation from monoclinic phase to tetragonal phase, and the large volume change in the opposite direction during cooling, it is easy to cause product cracking, which limits the application of pure zirconia in the high temperature field. However, after adding stabilizer, tetragonal phase can be stable at room temperature, so it will not change in volume after heating, greatly expanding the application range of zirconia. The raw material used as stabilizer in the market is mainly yttrium oxide.